Twitter announced on Thursday that it would be expanding “Birdwatch,” a crowdsourced project designed to combat misinformation.
Introduced last year as a pilot program, Birdwatch allows contributors who are in good standing with the social media company to address tweets they find misleading and provide context in the form of a note. Previously, notes created by the pilot’s 10,000 contributors appeared on a separate test site. As of March 3, however, the company says that a “small (and randomized) group of people on Twitter” in the U.S. will be able to see and rate the quality of the Birdwatch notes, according to a recent blog post.
For a note to show up in a tweet, it must be rated as helpful by enough Birdwatch contributors from different perspectives. Thanks to Twitter’s new partnerships with Reuters and The Associated Press, the quality of Birdwatch notes will also be assessed with feedback from the news agencies.
The announcement comes in the midst of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine — unverified information has easily spread on social media platforms and Russia is known for its robust use of misinformation and propaganda. Misinformation on Twitter, in particular, has long been an issue, which is what led to the development of Birdwatch in the first place. This situation in Ukraine has also put a new emphasis on how other social media companies are responding.
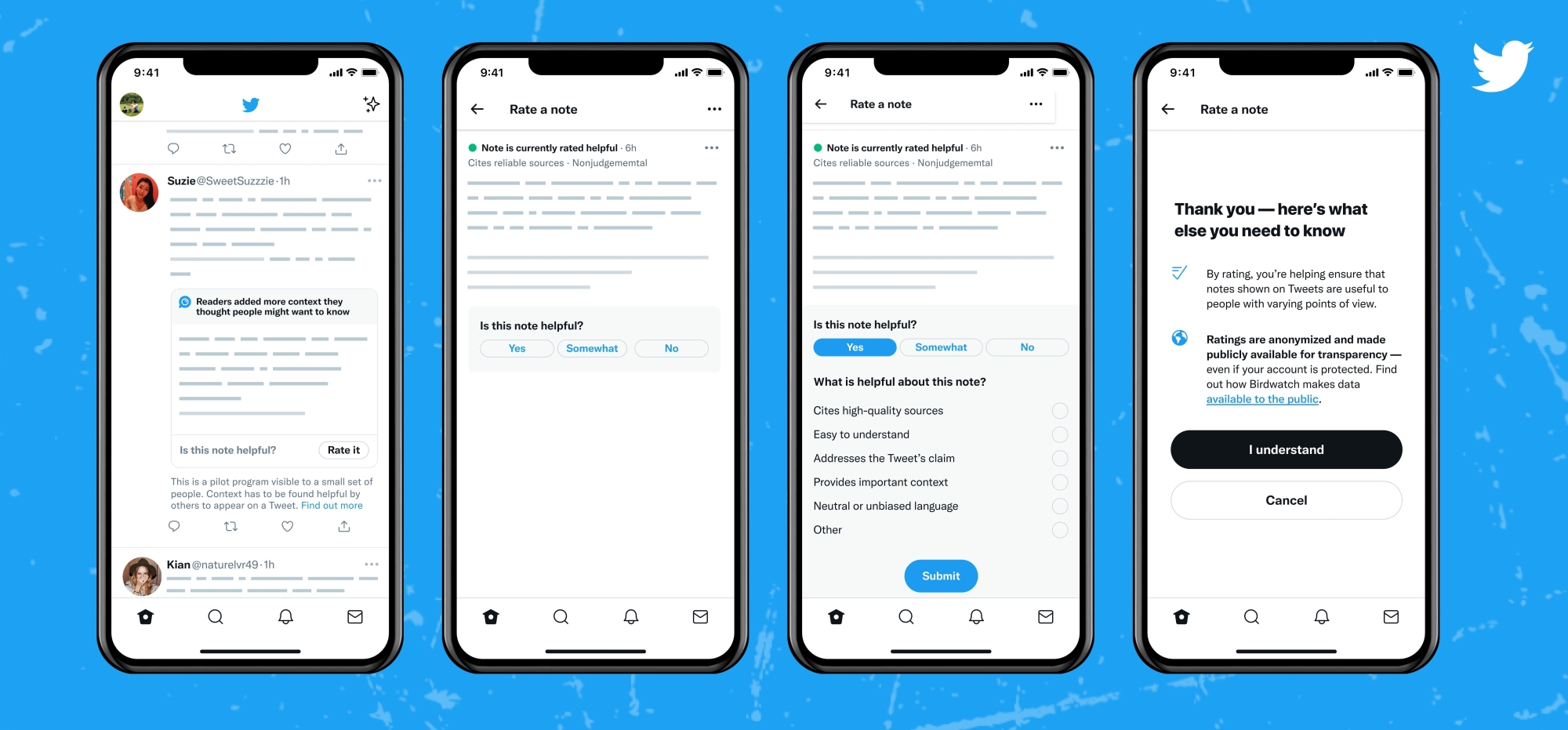
Birdwatch might be soon be showing up in your feed.
Credit: Twitter
The decision to expand the Birdwatch pilot is based on “promising results” from surveys with Twitter users, and feedback from the pilot contributors and academic researchers. According to an internal Twitter survey, “people were 20 to 40 percent less likely to agree with the substance of a potentially misleading Tweet after reading a note about it, compared to those who saw a Tweet without a note.” Examples of notes on the Birdwatch test site include contextualizing a quote from Vice President Kamala Harris who was explaining the complicated Ukraine/Russia situation in simplified terms to six-year-olds. Or noting that an image of Paul McCartney waving a Ukrainian flag onstage was from 2008.
With Birdwatch and other features, Twitter appears to be more proactive in fighting the spread of misinformation. But the question of its efficacy remains. According to The Washington Post, only about 43 tweets a day were being flagged by Birdwatch contributors.